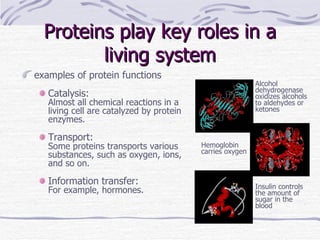
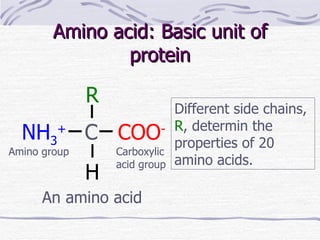
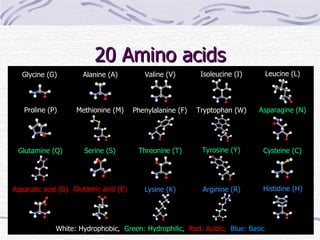
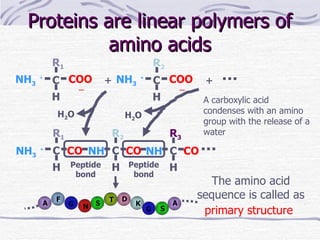
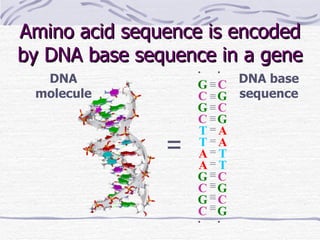
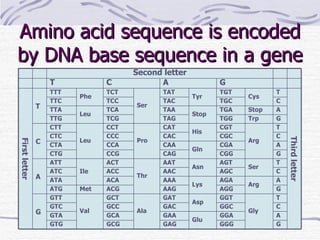
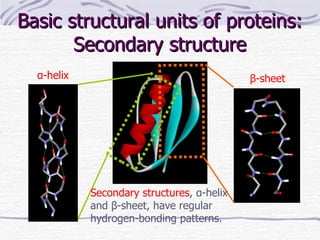
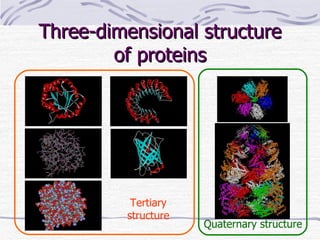
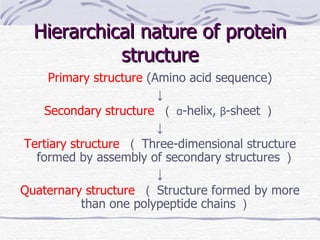
Proteins have many essential functions in living systems including acting as enzymes, transporters, regulators, and providing structure. There are 20 standard amino acids that make up proteins and their side chains determine each protein's unique properties. A protein's amino acid sequence is encoded in DNA and the sequence folds into complex three-dimensional structures that enable proteins to carry out their diverse roles.